Home
Systems Engineering
Subsea Control Systems
Software Development
Products and Applications
Tech Info
Contacts & Key Personnel
|
|
Products and Applications
ProLoop Control Loop Monitor
The Process IT Control Loop Monitor, ProLoop, is a tool for monitoring the performance of control loops.
Two versions are available:
ProLoop OPC
There are a number of performance criteria that can be examined:
- Integrated Error (IE)
The Integrated Error indicates how closely the process variable tracks the setpoint. If the
integrated error is close to zero, it indicates that the PV is, on average, close to the controller setpoint.
- Integrated Absolute Error (IAE)
Even though the integrated error (IE) may indicate that the average PV is close to setpoint,
there may, however, be cyclic deviations around the mean.
The Integrated Absolute Error indicates the extent to which the PV deviates from setpoint.
- Output Variation
This indicates the extent to which the controller is varying its output around the mean in an
effort to keep the process variable at setpoint. This is an important parameter when considering
valve wear. It may also indicate that the controller gain is set too high (in other words, the
proportional band is too small) as it is too sensitive to changes in the PV.
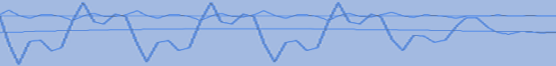
Sample Data
A closed-loop control loop simulator was used to generate PV, SP and OP for a PID controller:

The Control Loop Monitor indicates a number of characteristics of the loop:
- Integrated Error (IE)
This is close to zero (-0.03%), and indicates that, on average, the
loop is operating close to setpoint. The Integrated Error can, however, be misleading, as
it can be seen that the PV is cycling around the setpoint.
- Integrated Absolute Error (IAE)
This is substantially greater than the Integrated Error, and
indicates that the loop is deviating significantly from setpoint. The reason that IAE is so large compared with
IE is that the PV is cycling around the setpoint.
- Output Integrated Absolute Variation (OpIAbsVar)
This indicates that the controller
is moving the output significantly as it attempts to control to setpoint.

ProLoop AM
ProLoop has also been implemented in the Honeywell Application Module (AM). The AM implementation
uses custom data points, with one AM custom point processing a regulatory PID control point in the
control device. A HPM Regulatory Control point is shown here, but it could be a MFC or Extended Controller
regulatory control point on a Data Hiway.

The AM application consists of the following:
- ProLoop.AO
CL block that performs the control loop monitoring
- ProLpCDS.CL
Custom Data Segment (CDS), used for storing results and intermediate calculations
- ProLpPL.CL
Parameter List, required for compiling the CDS on the target system
One AM custom point is then built for each controller that is to be monitored. The code is generic, such
that adding a new AM point only requires linking the CL object code, not a recompilation.
Calculated parameters such as Integrated Error, Integrated Absolute Error and
Average Output Variation are stored in the CDS:
parameter IE : number "Integrated Error"
access engineer
eu "%"
parameter IAE : number "Integrated Absolute Error"
access engineer
eu "%"
parameter OpAvg : number "Average Output"
access engineer
eu "%"
parameter OpVarAvg : number "Average Output Variation"
access engineer
eu "%"
parameter AlarmFlg : AmFlag "Alarm Flag"
access engineer
parameter IAETP : number "Integrated Abs Error Trip Point"
access engineer
eu "%"
value 2.0
parameter OpVarTP : number "Output Variation Trip Point"
access engineer
eu "%"
value 2.0
An alarm can be raised, via the point in the AlarmFlg parameter, if these calculated variables
exceed the alarm trip point.
|